Here, we discuss some of the most common signs that a concussion has occurred (and it’s time to see a doctor):
- Headache. If you’ve hit your had or experienced whiplash, you probably wouldn’t be surprised if you have a headache afterward. This symptom occurs in 95% of people who experience a concussion, but the type and severity of headache can vary from one person to another. One may feel pressure in the head while another may feel like their pain is expanding outward, like a balloon blowing up.
- Nausea. A concussion occurs when the brain has sustained a traumatic injury. As a result, the head pain that occurs may be accompanied by nausea or even vomiting. If vomiting occurs right away after an injury, it may indicate Vestibular dysfunction or could point to a significant neurological impact. Nausea that develops later and persists is usually related to migraine pain. Though not a serious problem, it can be very uncomfortable.
- Physical and Cognitive Impairment. Even a mild concussion can have physical and cognitive effects. Examples include a sense of fogginess and the inability to concentrate or process thoughts. A person may have memory lapses or difficulty, may feel confused, have slurred speech, feel dizzy, and have difficulty walking. These symptoms may be noticeable right after the injury or may develop later.
What Happens After a Concussion?
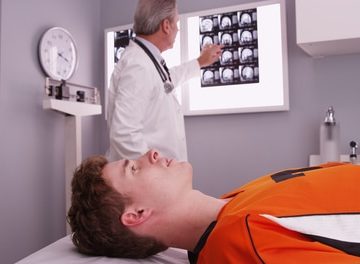
For the most part, concussion treatment is about watching and waiting and treating symptoms appropriately. Depending on the symptoms a patient presents with, a doctor may order imaging of the head, such as an MRI. Then enhances the examination by showing the internal aspects of the brain and head that may be affected by not yet showing signs of impairment. In addition to providing patients with medication or guidance regarding over-the-counter medications or supplements to promote comfort and more expedient healing, a doctor may also advise against going to school or work. People who are still having symptoms of a concussion should absolutely avoid driving or using heavy machinery. The concussed brain may have difficulty processing information for some time and should not be stressed in any way until this processing improves. This means students will need to stay home from school and avoid texting, doing homework, and engaging in stressful activities of any kind. During this time, the doctor may schedule periodic follow-ups to assess recovery and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
If you think you or your child has a concussion, contact Orthopedic Associates of Long Island. You can schedule a consultation with a concussion specialist at 631.689.6698.